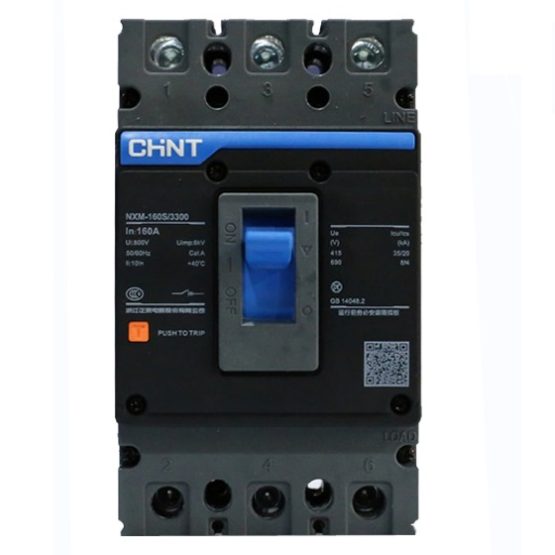
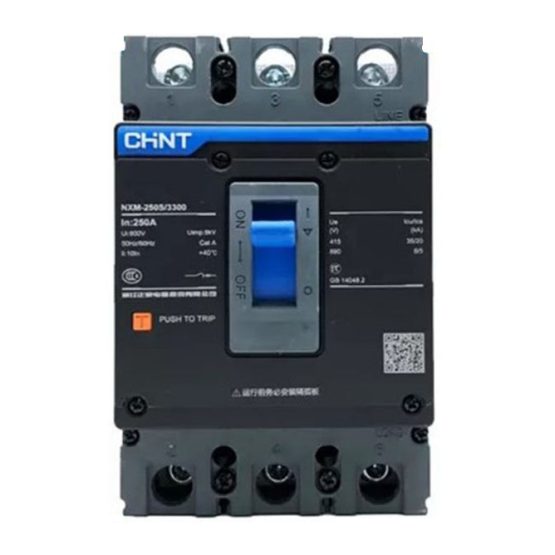
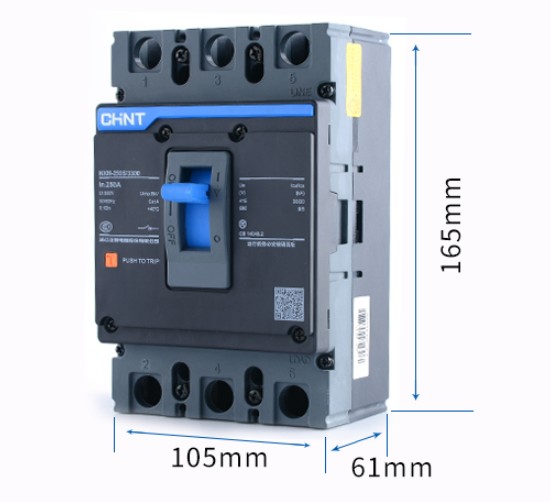
Chint Moulded Case Circuit Breaker 3 Pole (NXM-125 S) 125 Amp
Rs 12,000.00
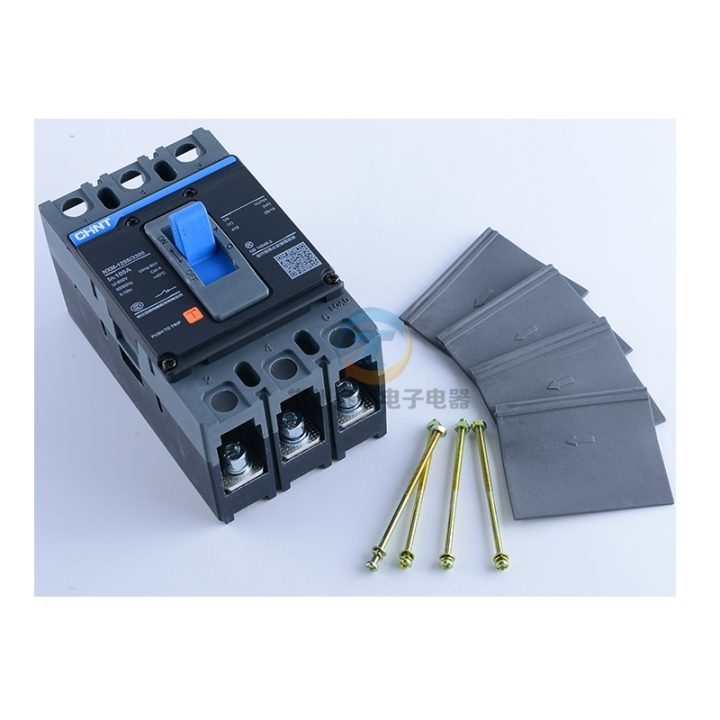
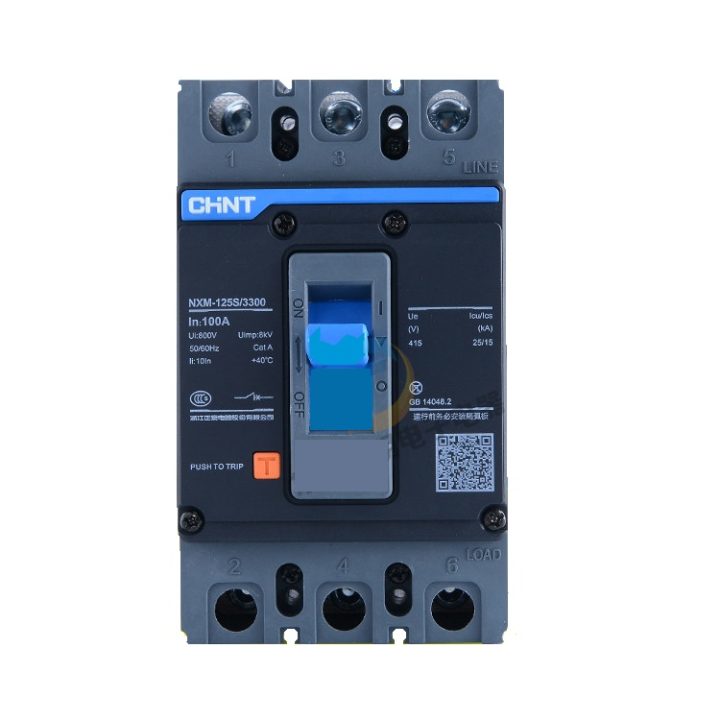
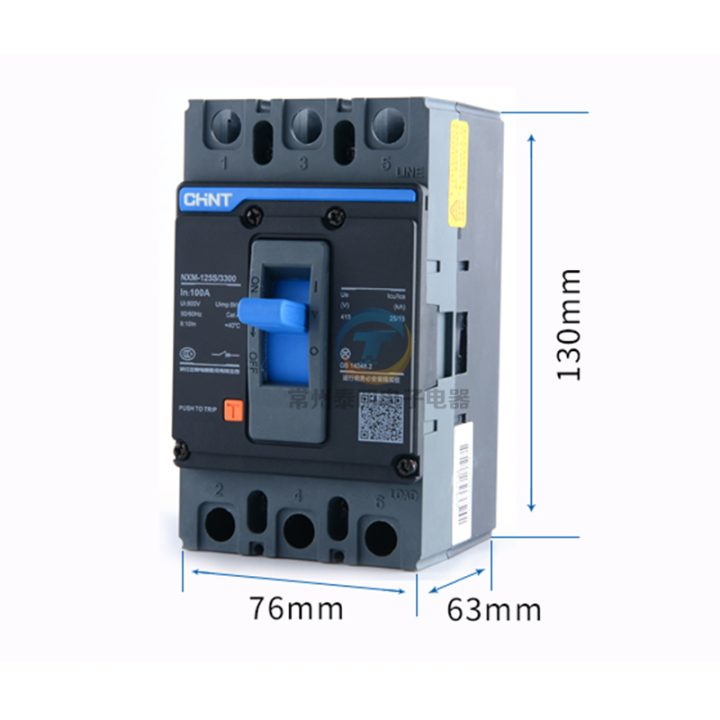
Product: MCCB (moulded case circuit breaker) 3 pole
Brand: Chint
Model: NXM-125 S
Number of pole: 3
Rated Current: 125 Ampere
Frequency: 50/60 Hz
Rated Short-Circuit Breaking Capacity: 25 kA (25000A)
Mounting: with screw
Mounting mode: vertical or horizontal
Type: fixed
Certificates: KEMA, ESC, UKrSEPRO, PCT, RCC, KC
Standard: IEC/EN 60947-2
- Description
- Reviews (0)
Description
Description
Reviews (0)
- This moulded case circuit breaker (MCCB) is a type of electrical protection device that is used to protect the electrical circuit from excessive current, which can cause overload or short circuit.
- With a current rating of up to 2500A,
- MCCBs are used mostly in industrial areas on high voltage and heavy duty machinery.
- These breakers are used instead of miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) in large scale PV systems for system isolation and protection purposes.
- The MCCB uses a temperature sensitive device (the thermal element) with a current sensitive electromagnetic device (the magnetic element) to provide the trip mechanism for protection and isolation purposes.
- This enables the MCCB to provide:
- Overload Protection,
- Electrical Fault Protection against short circuit currents, and
- Electrical Switch for disconnection.
Sizing
- MCCBs in an electrical circuit should be sized according to the circuits expected operating current and possible fault currents.
- The three main criteria while selecting MCCBs are:
- The rated working voltage (Ue) of the MCCB should be similar to the system voltage.
- The trip value of the MCCB should be adjusted according to the current drawn by the load.
- The breaking capacity of the MCCB must be higher than the theoretical possible fault currents.
Purpose of trip Button
- This test is conducted by testing the response of the MCCB under simulated over-current and fault conditions.
- Thermal protection of the MCCB is tested by running a large current through the MCCB (300% of rated value).
- If the breaker fails to trip, it is an indication of failure of thermal protection.
- The test for magnetic protection is conducted by running short pulses of very high current.
- Under normal conditions, magnetic protection is instant.
- This test should be conducted at the very end as high currents increase the temperature of contacts and insulation, and this may alter the results of other two tests.


























Reviews
There are no reviews yet.